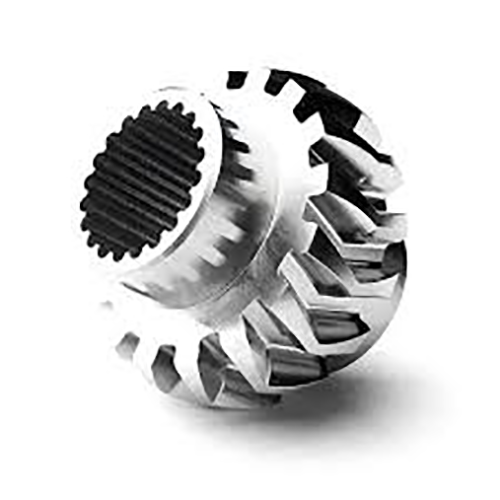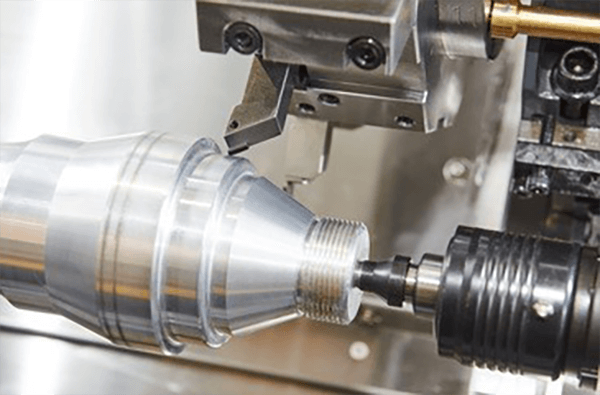
Achieving specified outer texture for a fabricated unit proves indispensable.
- Design documents set out definitive finishing requirements for parts
- Many specifications reference Ra, an average roughness metric, for surface measurement
- Decoding surface notes is important for ensuring components achieve required performance
- Clear finish specification affects lubrication behavior, sliding resistance, and lifespan
- It is essential to interpret the specific callout to achieve the desired outcome
Understanding Precision Engineering in CNC Machining

CNC-driven fabrication functions as a modern manufacturing method using CNC instructions the equipment fabricates detailed forms with consistency.
- CNC systems permit manufacture of precise components from diverse substrates
- CNC adaptability suits industries including aerospace and automotive sectors
- G-code driven machining maintains reliable consistency across batches
From early-stage prototyping through mass manufacturing CNC machining underpins modern fabrication
Comprehending CNC Machine Specifications
Understanding equipment specifications can look intimidating initially
In contrast, measured learning and order help you traverse technical specifications
Kick off by isolating primary specs such as rpm, feed, tolerance, workspace, controller
Each of these specifications contributes to the machine's overall performance.
As an example, increased spindle rpm favors soft alloys and higher feed favors throughput.
Comprehending those interactions assists in picking the proper CNC for tasks
Take time to inspect maker literature meticulously.
Manufacturer docs typically supply key details and decode technical phrasing
Comprehensive Guide to CNC Machinery
Computer numerical control machines denote software-driven tools for precise automated fabrication of many substances They read numerical control code to orchestrate cutter motion and axis control.
- Representative CNC types cover milling tools, turning machines, routers, plasma cutters
- Cutting methods suit steels, plastics, woods, and layered composites
- Plus CNC technology provides rapid prototype cycles and limited manufacturing for small firms and research units
Fundamental CNC Machine Concepts
They demonstrate convergence of tight hardware tolerances and refined software control Flexible equipment harnesses software instructions to automatically fabricate basic components and intricate assemblies Underlying principle converts virtual designs into actual manufactured items.
- Numerical control manufacturing
- Programmed manufacturing process
It comprises controlled axis moves directed by programmed code Skilled staff determine cutting conditions, observe operations, and verify finished part quality.
Surface Finish's Importance in CNC Machining
Attaining target texture in CNC processes is critical It greatly affects the final product's performance as well as its aesthetics Workpiece material, tool settings, and secondary finishing processes determine texture.
Superior polishing extends service life; rougher finishes may limit capability Numerical control machining supplies multiple methods and cutters to obtain target textures.
- Example: altering tool nose radius and flute profile |carbide alloys|surface speed choices to reach texture
- Also surface treatments such as grinding and polishing can refine textures
Comprehending the connections between machining choices and texture secures better results.
From Operation to Applications: CNC Basics
Precision production uses machine control software to shape parts from different material classes They process digital commands to produce elaborate components repeatedly Grasping G-code, tool selection, and machine operation underpins successful manufacture
Applications of CNC machining are incredibly diverse spanning numerous industries such as aerospace automotive manufacturing From intricate propeller parts to exacting mold inserts, CNC produces accurate geometries
Callouts and Surface Roughness for CNC Parts
Exact finish callout is important for CNC component manufacturing It makes sure the product satisfies function and aesthetic demands Drawings usually depict finish requirements with Ra roughness values Measured in micrometers or inches, the number reflects mean surface roughness height.
Factor in desired smoothness and the component’s functional purpose when setting finish callouts

For instance a smooth surface finish might be preferred for parts that require tight tolerances or precise alignment
Rugged finishes sometimes serve parts that need enhanced traction or grip
Use explicit finish instructions on design documents to convey the surface requirement Document the Ra value and enumerate any extra finishing or treatment instructions.
Consider that thorough finish callouts underpin quality manufacturing
Varieties of CNC Machines and Capabilities
The CNC ecosystem includes a broad selection of machines for multiple task categories They pair with CAD software to translate designs into cutting commands for precise fabrication.
- Milling machines are renowned for their ability to remove material from a workpiece shaping it into complex geometries
- Lathes excel at producing round parts such as shafts rods and bushings
- Beam and jet cutting methods enable accurate slicing with differing thermal impacts
Choosing the right CNC depends on production goals material type and required accuracy Different CNC platforms supply distinct functionality valuable across industries including automotive and aviation.
Achieving Premium Surface Results in CNC Processes
Obtaining fine surface quality is important and CNC technology delivers consistent control to attain it Using accurate feed and speed selection plus optimized tool geometry technicians refine cutting action to reduce surface flaws Plus durable cutting materials and appropriate coolant control boost finish quality Through careful selection of cutting strategies and meticulous machine setup CNC machining enables the creation of components with exceptional surface quality for diverse applications.
Surface Finish Considerations in CNC Programming
Tuning code to influence finish plays a central role in meeting quality aims Feed, spindle settings, and cutter design are major drivers of the final surface condition Meticulous parameter tuning together with suitable coolant use promotes smoother finishes.
- In addition periodic tool servicing and checks secure consistent surface quality Continuous tool maintenance and oversight preserve high finish consistency Additionally routine tool checks and upkeep cnc machine definition maintain consistent finish quality
- To improve surface outcome account for material, roughness target, and application
- Virtual simulation provides a way to optimize feeds and speeds before cutting
- Additionally routine tool checks and upkeep maintain consistent finish quality
